🏃 Ceptron-mov is a study project that aims to apply Machine Learning and Data Science concepts to build a human-machine interface that is capable of identifying human physical movements.
📺 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CSnNmrJZ-oU&t=4s
obs: The results spoken in the video are in Portuguese (pt-BR). The labels of movements in the dataset as well.
The availability of a system capable of automatically classifying the physical movements performed by a human being is extremely attractive for many health monitoring applications and for the development of advanced man-machine communication interfaces. When we speak of physical movements, I mean whether the person is sitting, lying down, walking, running, pedaling, and so on.
Information on physical movements is valuable as a source of contextual knowledge. If this information were available, the interaction between man-machine would be richer. In robotics, there are several applications that require the robot’s ability to recognize which movement the user wants to perform. For example, smart walking support systems, which help people with motor disabilities and the elderly while trying to walk or walk.
To create a system of classification of physical movements automatically, the main feature is the motion sensors. These sensors should be small and light and be in contact with the human body. Smartphones have several sensors on board, like two of the main ones used in this work, the accelerometer and the gyroscope. With the great growth of people using the mobile device, it is the ideal device to perform movement recognition.
- Android and Sensors API Android to develop the application that communicates with the sensors (Accelerometer and Gyroscope) of the smartphone to monitor the movements and collect the data.
- Firebase Database to store data collected by Android sensors.
- Jupyter Notebook to document the extraction of features and analysis of machine learning models.
- Python3 taking the data collection, the rest of the project was all developed in python.
The Python libraries below are required to run the project.
Run the following command to install:
$ pip install -U numpy scipy scikit-learn matplotlib pandas Flaskobs: The Anaconda distribution of python already has the above and most included packages.
This project has 4 applications.
-
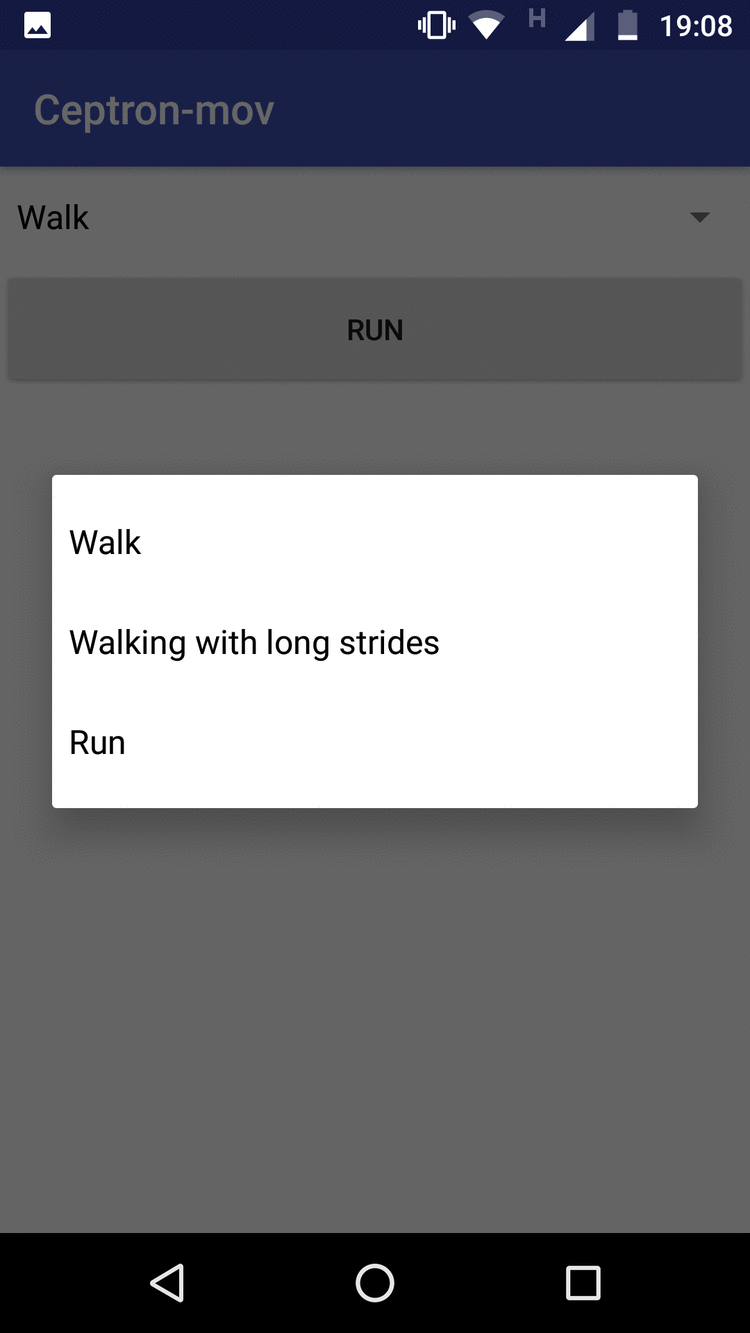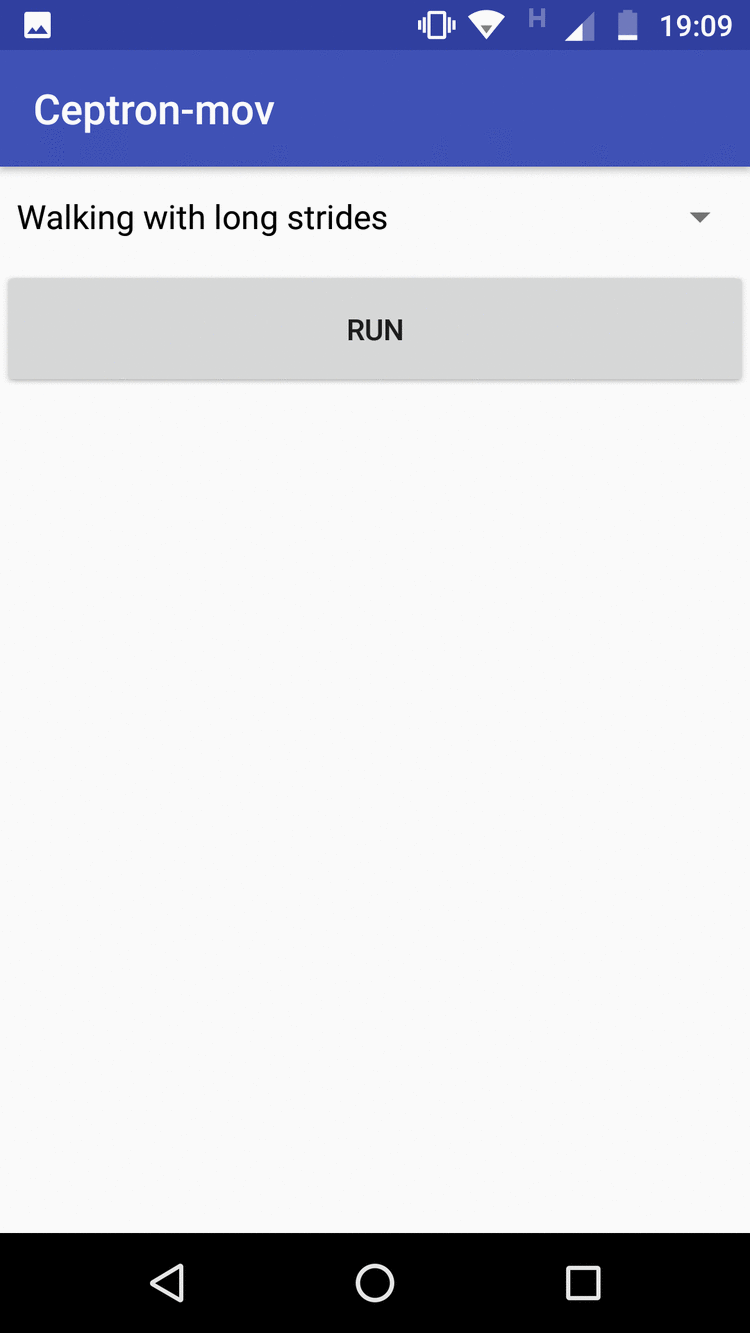
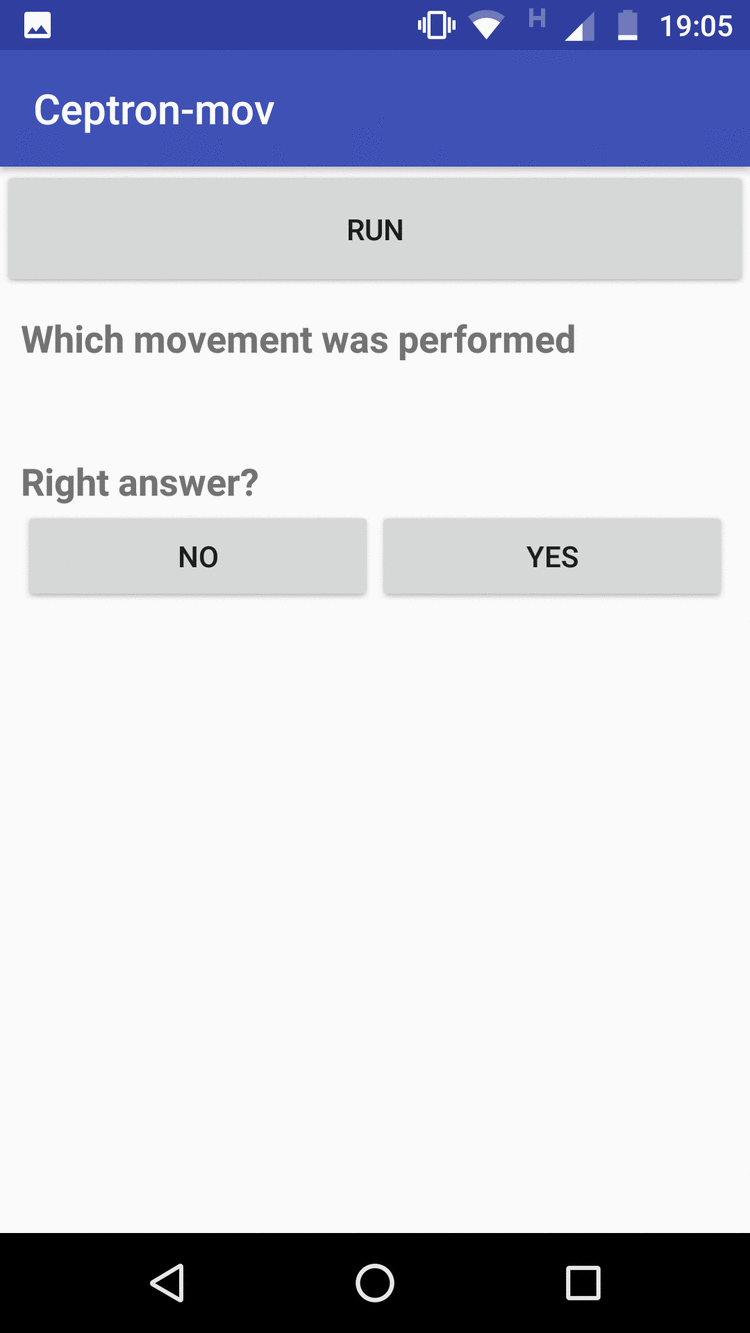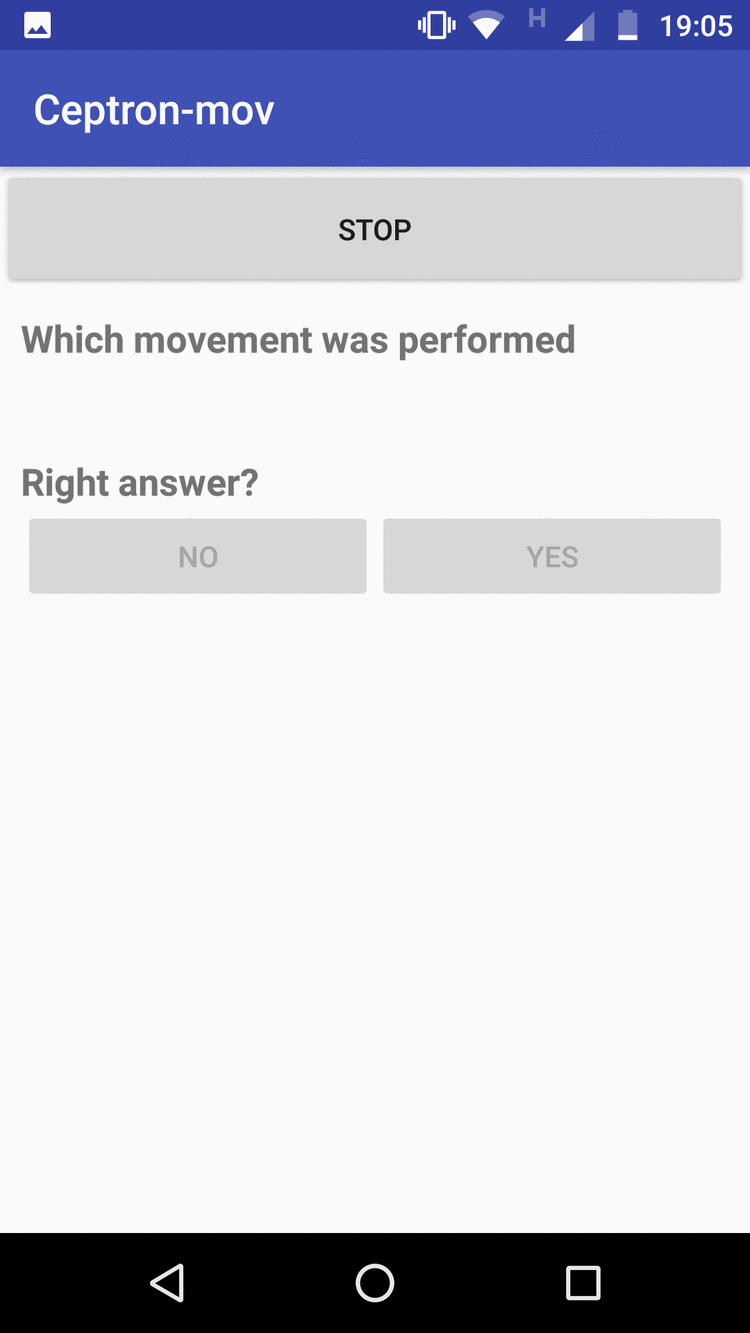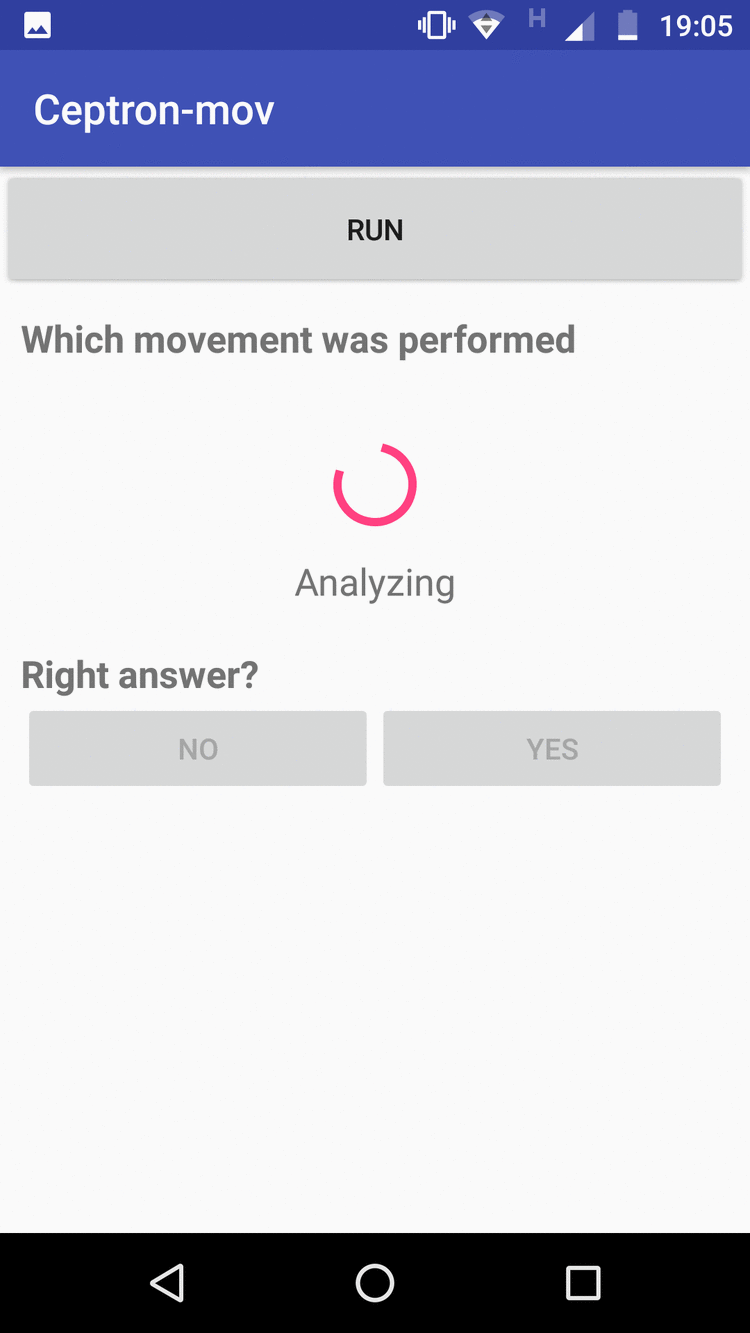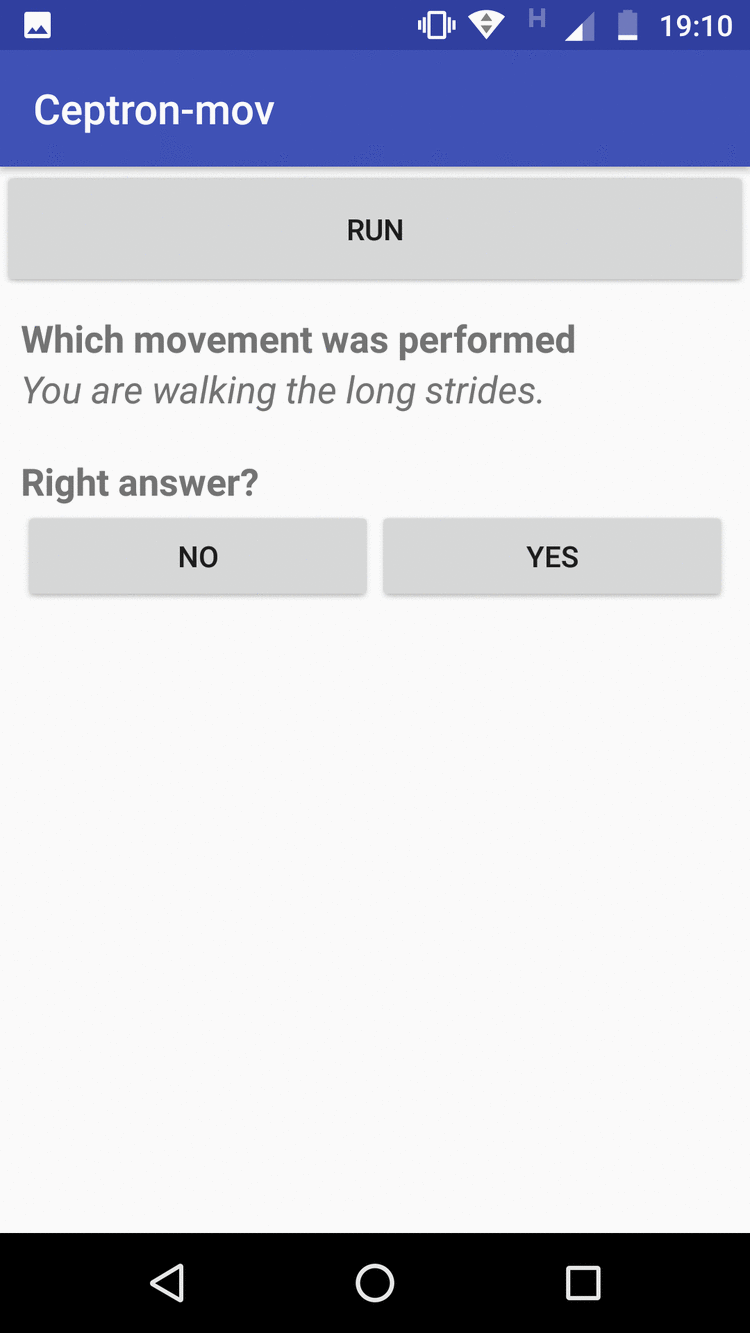
App-mobile: It collects the data according to the movement that the user has informed by a selector of movements, then it clicks to execute the application to begin to monitor the movements, and when the movement finishes, it stops clicking and the data is sent to the Firebase automatic. The application also implements a way to evaluate the machine learning model that has been trained. The user clicks run, makes the move. To see the answer, he clicks to stop when he finishes making the move. When Stop is clicked, the template will respond to what movement has been made. If it hits, the user marks as True Positive, if not, it marks as False Positive
The figure on the left shows the data collection screen and the one on the right shows the evaluation screen for new entries.
-
SRC/API: Api is a rest service that implements the trained model, and receives app evaluation data to classify a new entry.
To run the API, navigate to the project folder and run the command below:
$ python -m api
-
SRC/Intra: The project below is responsible for preprocessing the raw data, and extracting raw data characteristics to assemble the training data set.
To run the Intra project, navigate to the project folder and run the command below:
$ python -m intra
-
Notebooks: It documents the characteristics used and explains each one of them. It also documents any analysis of the chosen models to see which makes the best data modeling and which one performs best.
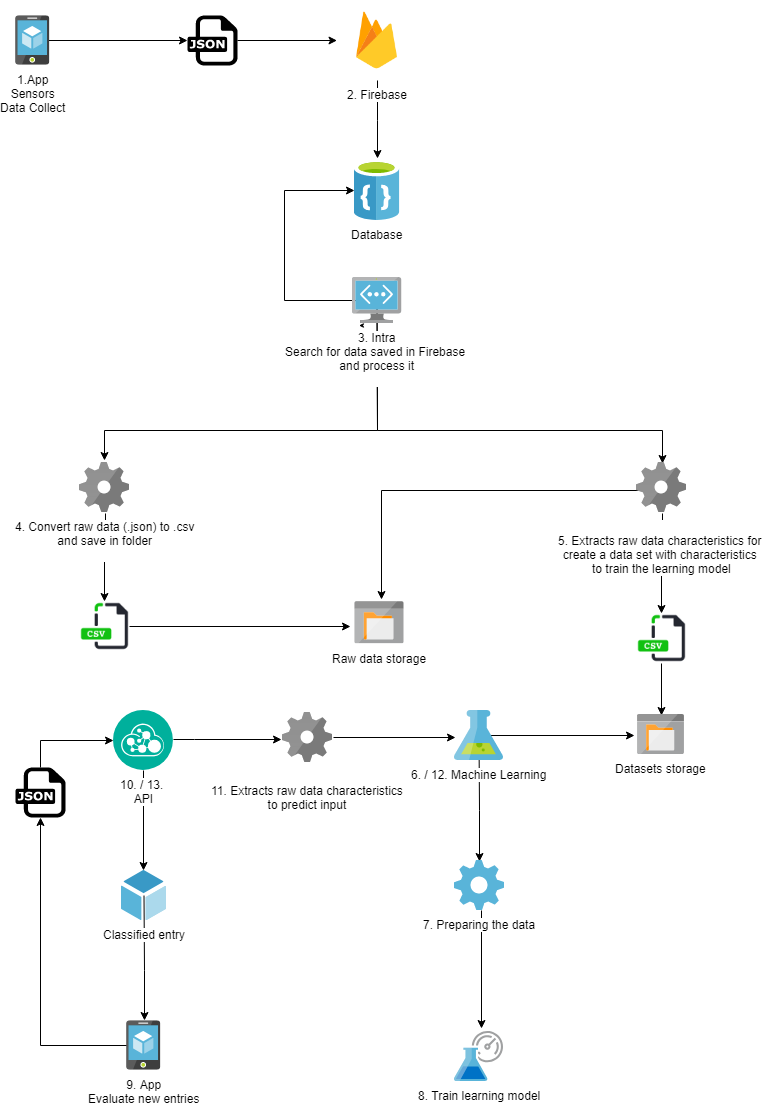
This basis demonstrates the process from data collection to the movement of a machine learning model.
-
The application sends the data collected from the sensors in json format to Firebase.
-
Data is saved in the Firebase Database service.
-
With data saved in the Firebase database, the application responsible for fetching and processing data online is executed.
-
The process receives the data in .json format and converts the file to .csv, and assembles a structure (The structure is described in detail in the notebook * Acquisition of characteristics *) in the file that will be used to extract the characteristics.
-
The Extraction process reads all the files containing the raw data and extracts the characteristics (The extraction of characteristics is described in detail in the * Characteristics * book) relevant to the movements, and creates the data set. After extraction, the data is written in .csv format and saved in the dataset folder.
-
To train the learning model, the dataset is loaded from the datasets folder.
-
The data is prepared before starting the training.
-
Train the machine learning model.
-
After the model is trained, the evaluation application sends the new data in json format to the classification service.
-
The service receives the data, and sends to process them and extract the characteristics.
-
The service receives the data, and sends to process them and extract the characteristics.
-
Predicts entry
-
Returns which movement was executed for the application.